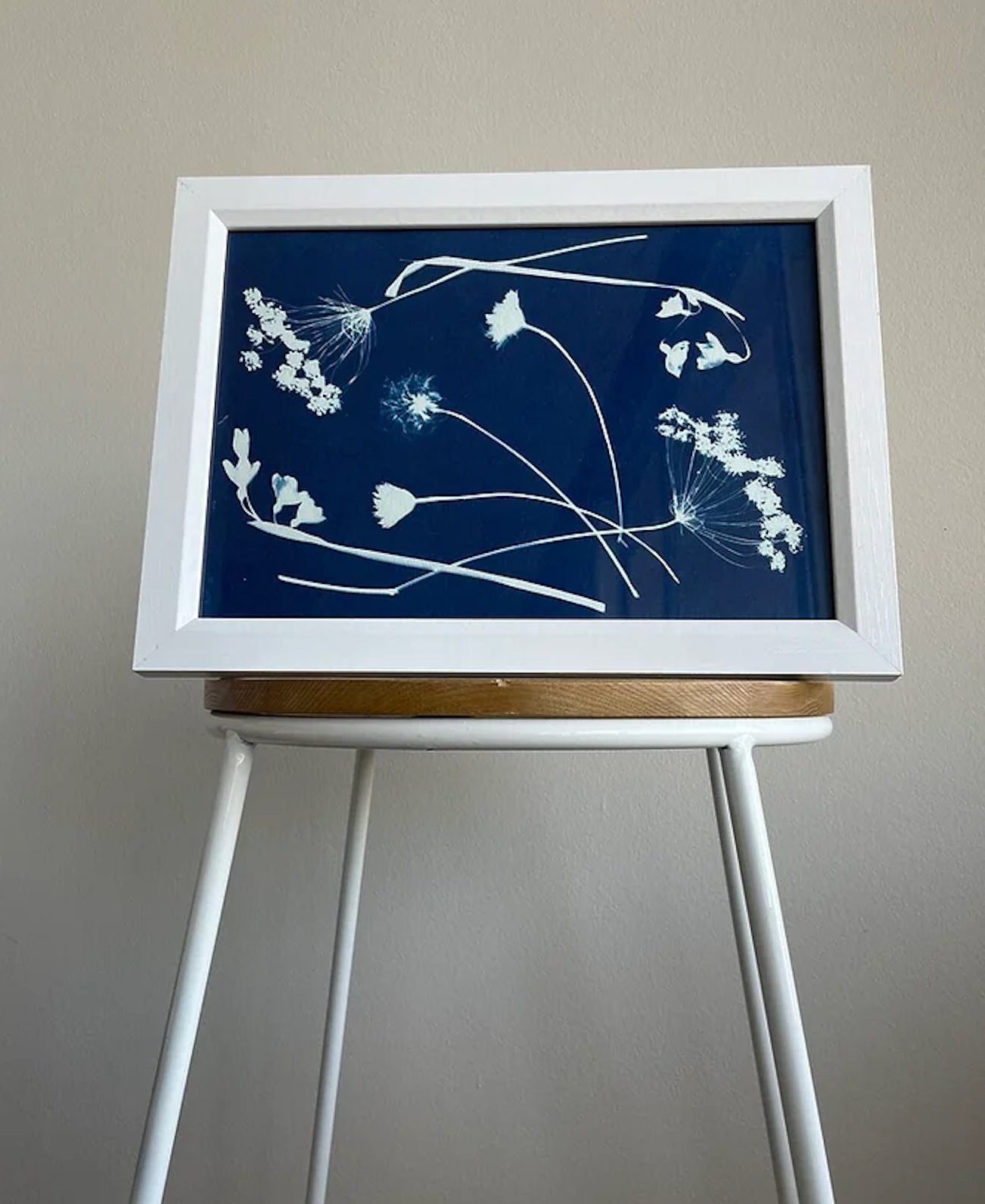
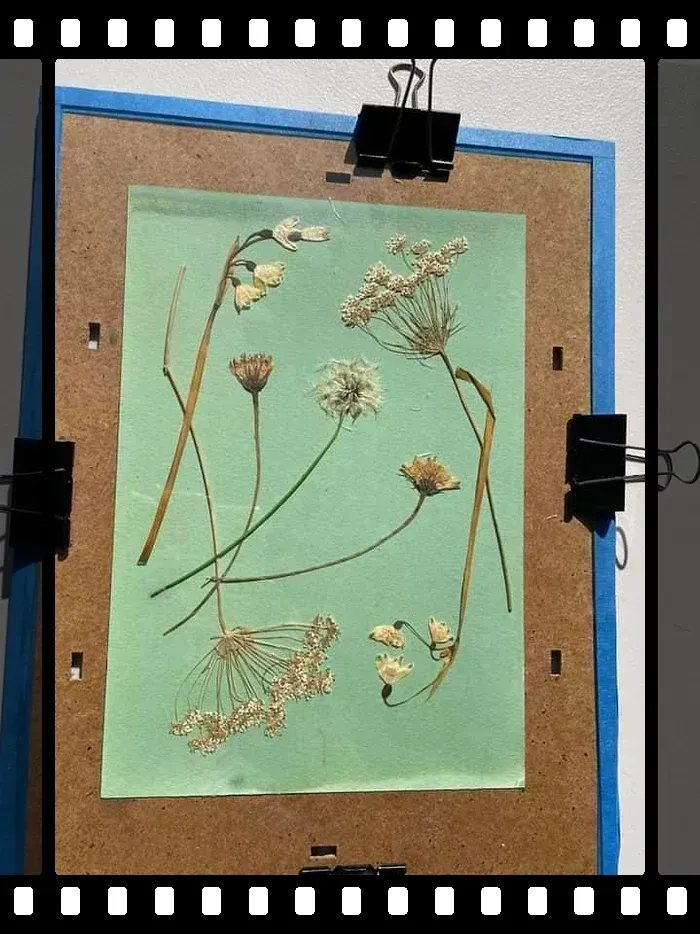
The blue is a result of chemicals and their reaction to sunlight.
To create a blueprint you draw your original design on a semi-transparent piece of paper or cloth, and place it on top of paper that has been treated with a mixture of two chemicals; potassium ferrocyanide and ammonium iron citrate. This is a photosensitive (and very hazardous) chemical mixture.
Then, you take the stacked pieces of paper and expose them to bright ultraviolet light (like the sun). The treated paper turns blue, but the lines of the original drawing block out the sun's effects and leave white lines on the treated paper. After only a few minutes of exposure, you are left with a perfect copy.
The reaction from the sun causes a compound to appear on the paper called blue ferric ferrocyanide, or Prussian Blue. This is the blue colour left behind on the treated paper and why these copied documents came to be known as blueprints. The soluble chemicals would then be washed off, according to New World Encyclopedia, and you are left with a very stable copy.